ABOUT CANCER

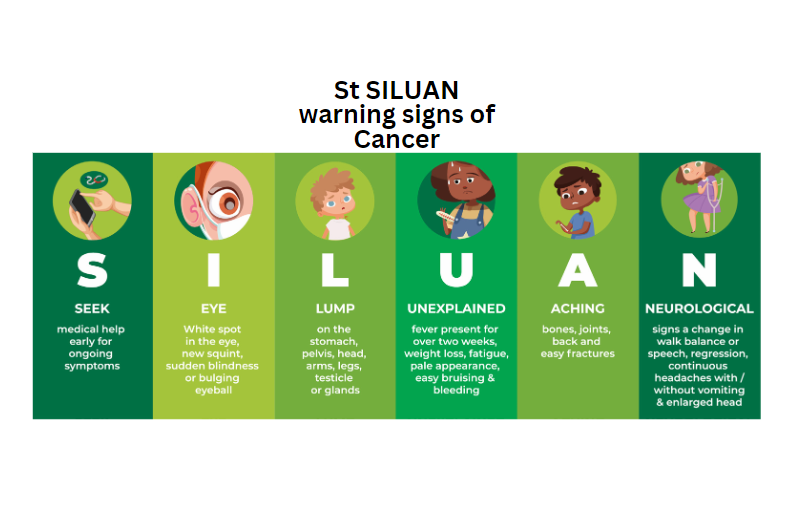
Cancer stands as the second most prevalent cause of global mortality, claiming the lives of 10 million individuals annually.
Over 40% of cancer-related deaths are deemed preventable, given their association with modifiable risk factors like smoking, alcohol consumption, inadequate diet, and physical inactivity.
Approximately one-third of all cancer-related fatalities could be averted through regular screening, along with prompt detection and intervention.
Alarmingly, 70% of cancer deaths transpire in low-to-middle income nations. The implementation of tailored strategies for prevention, early identification, and treatment has the potential to rescue millions of lives each year.
Childhood Cancer
Childhood cancer is a harsh reality affecting the lives of over 3 lakh children globally each year, emphasizing the urgent need for awareness, research, and support. In India, more than 50,000 new cases of childhood cancer are reported annually, underscoring the scale of this health challenge.
Children facing cancer require specialized care provided by pediatric cancer units equipped with dedicated disease management groups. The age group of 0-14 is particularly vulnerable, although some centers extend their services to individuals up to 18 years old. This critical period demands tailored treatment approaches that not only address the physical aspects of the disease but also consider the unique emotional and psychological needs of young patients.
The impact of childhood cancer extends beyond the affected child, affecting families, friends, and communities. The journey through diagnosis, treatment, and recovery is a challenging and emotional rollercoaster that requires immense strength and resilience. Support networks play a crucial role in helping families navigate the complexities of pediatric cancer, offering emotional support, financial assistance, and resources for coping with the long-term effects of treatment.
Advancements in medical research have improved the prognosis for some childhood cancers, but much work remains to be done. Funding for research, access to quality healthcare, and awareness campaigns are vital components in the ongoing battle against childhood cancer. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes, making education and awareness crucial in saving young lives.
Childhood Cancer Day, observed on February 15th, serves as a rallying point for communities worldwide to join forces, spread awareness, and advocate for better resources and support systems for children fighting this formidable adversary. By fostering a global commitment to pediatric cancer research and care, we can aspire to a future where no child's life is cut short by this devastating disease.
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer, a prevalent and potentially life-threatening condition, arises from the abnormal growth of cells in the breast tissue. It primarily affects women, but men can also develop this malignancy, albeit less frequently. The key to managing and successfully treating breast cancer lies in early detection and intervention.
Risk factors for breast cancer include advancing age, genetic mutations such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, family history, and hormonal influences. Regular screenings, particularly mammograms, play a pivotal role in identifying abnormalities in breast tissue at an early, more treatable stage.
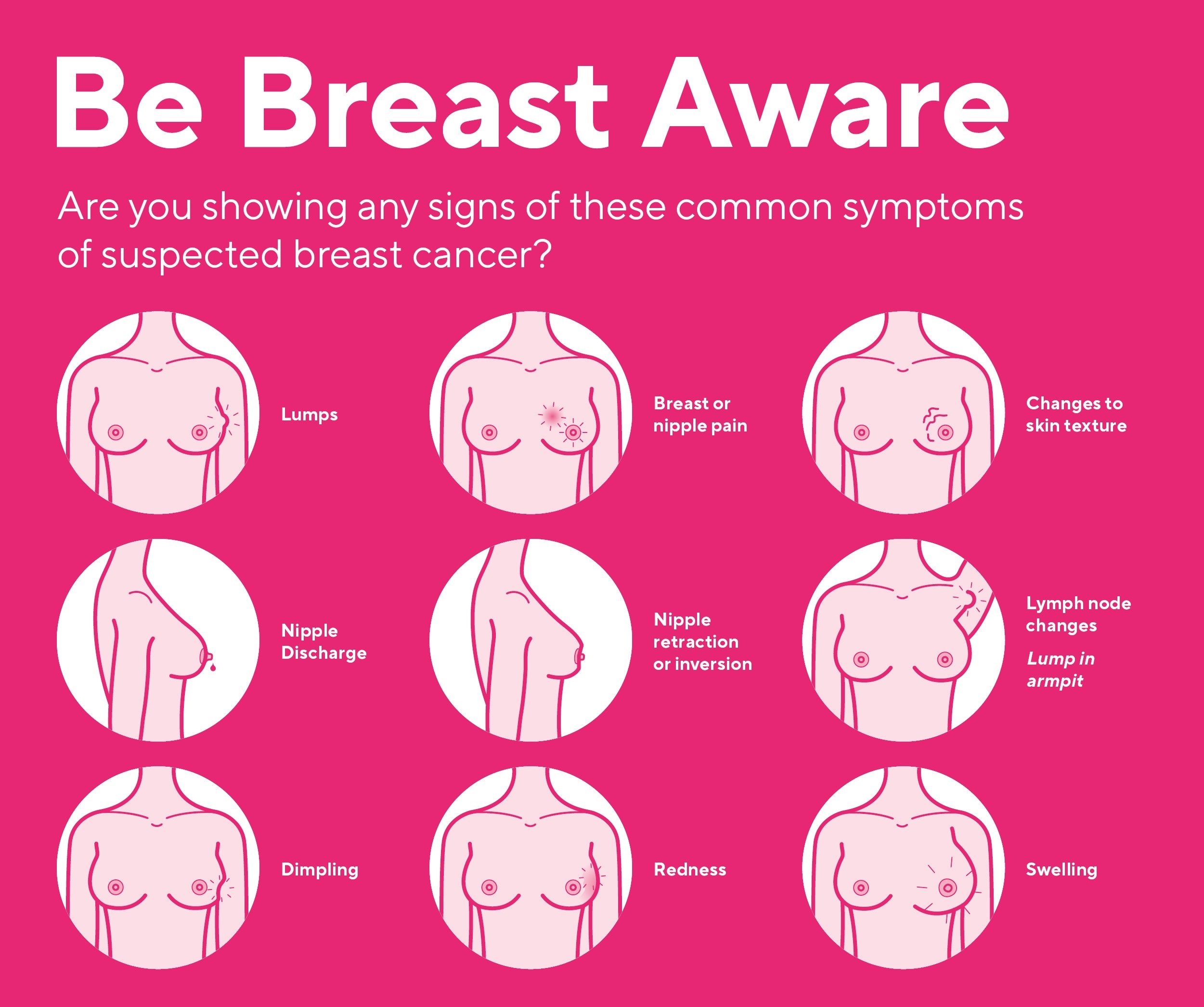
Common symptoms of breast cancer include the presence of a lump or thickening in the breast, changes in breast size or shape, and alterations in the skin's texture or appearance. Additionally, unexplained pain in the breast or nipple discharge may warrant further investigation.
Upon diagnosis, treatment strategies are diverse and depend on factors such as the stage of cancer, its specific characteristics, and the patient's overall health. Standard treatments encompass surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and hormone therapy. Advances in targeted therapies and immunotherapy have also expanded treatment options, contributing to more personalized and effective care.
Breast cancer awareness campaigns emphasize the importance of routine self-examinations, regular screenings, and understanding risk factors. These initiatives aim to empower individuals with knowledge, encouraging early detection, and fostering a proactive approach toward breast health.
Overall, advancements in research, awareness, and medical interventions continue to improve outcomes and reduce the impact of breast cancer on individuals and communities worldwide.
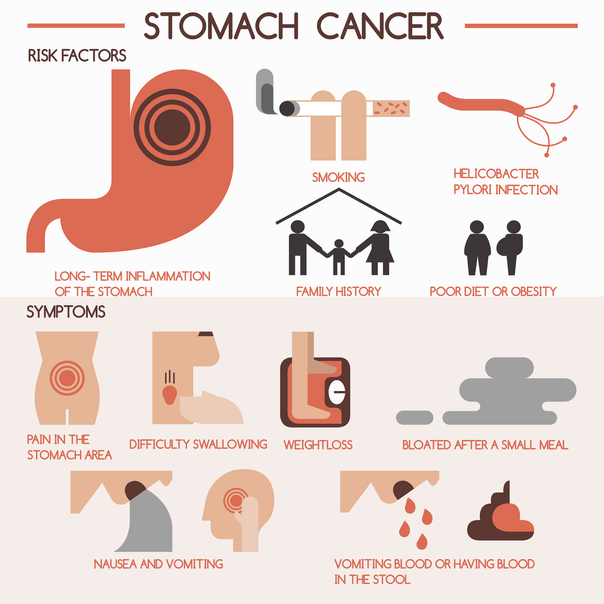
Stomach Cancer
Gastric cancer often presents minimal and rare early symptoms, typically emerging in advanced stages.
Indicators include indigestion, post-meal bloating, poor appetite, stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, blood in stool or vomit, weight loss, heartburn, yellowing of eyes and skin, difficulty swallowing, and anemia.
Stomach cancer treatment varies based on type and stage. Approaches encompass surgery for tumor removal, radiation therapy to eliminate cancer cells, chemotherapy using drugs to kill cancer cells, and targeted drug therapy disrupting cancer cell functions.
Stomach cancer, or gastric cancer, evolves slowly over years. The lifetime risk for men is approximately 1 in 95, and for women, it's about 1 in 154. Risk factors include age (common in late 60s to 80s), family history, male gender prevalence, and both inherited and acquired gene mutations. Increasing awareness of these factors can aid in early detection and treatment.
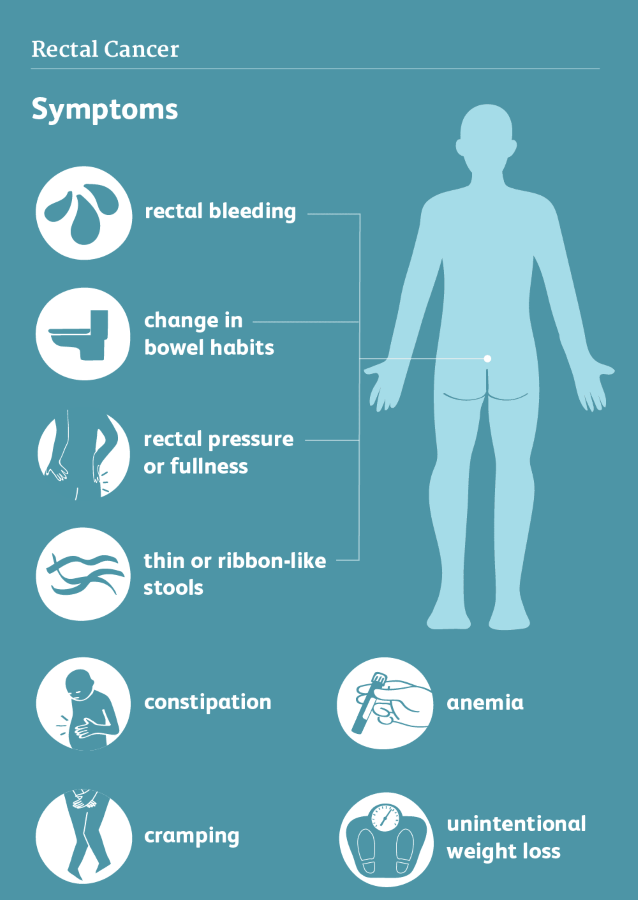
Rectal Cancer
Rectal cancer is a malignancy that develops in the rectum, the last portion of the large intestine. Early symptoms are often subtle, and diagnosis may occur at advanced stages.
Signs include changes in bowel habits, blood in the stool, abdominal discomfort, and unintended weight loss. Routine screenings, such as colonoscopies, are essential for early detection.
Treatment for rectal cancer depends on the cancer's stage and may involve surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy to target cancer cells, and chemotherapy to kill or control their growth. Additionally, targeted drug therapy may disrupt specific cancer-related processes.
Early intervention is crucial for successful outcomes, highlighting the importance of awareness and regular screenings. Risk factors include age, family history, inflammatory bowel diseases, and certain genetic conditions.
Adhering to a healthy lifestyle and seeking medical advice for concerning symptoms can contribute to better rectal cancer prevention and management.
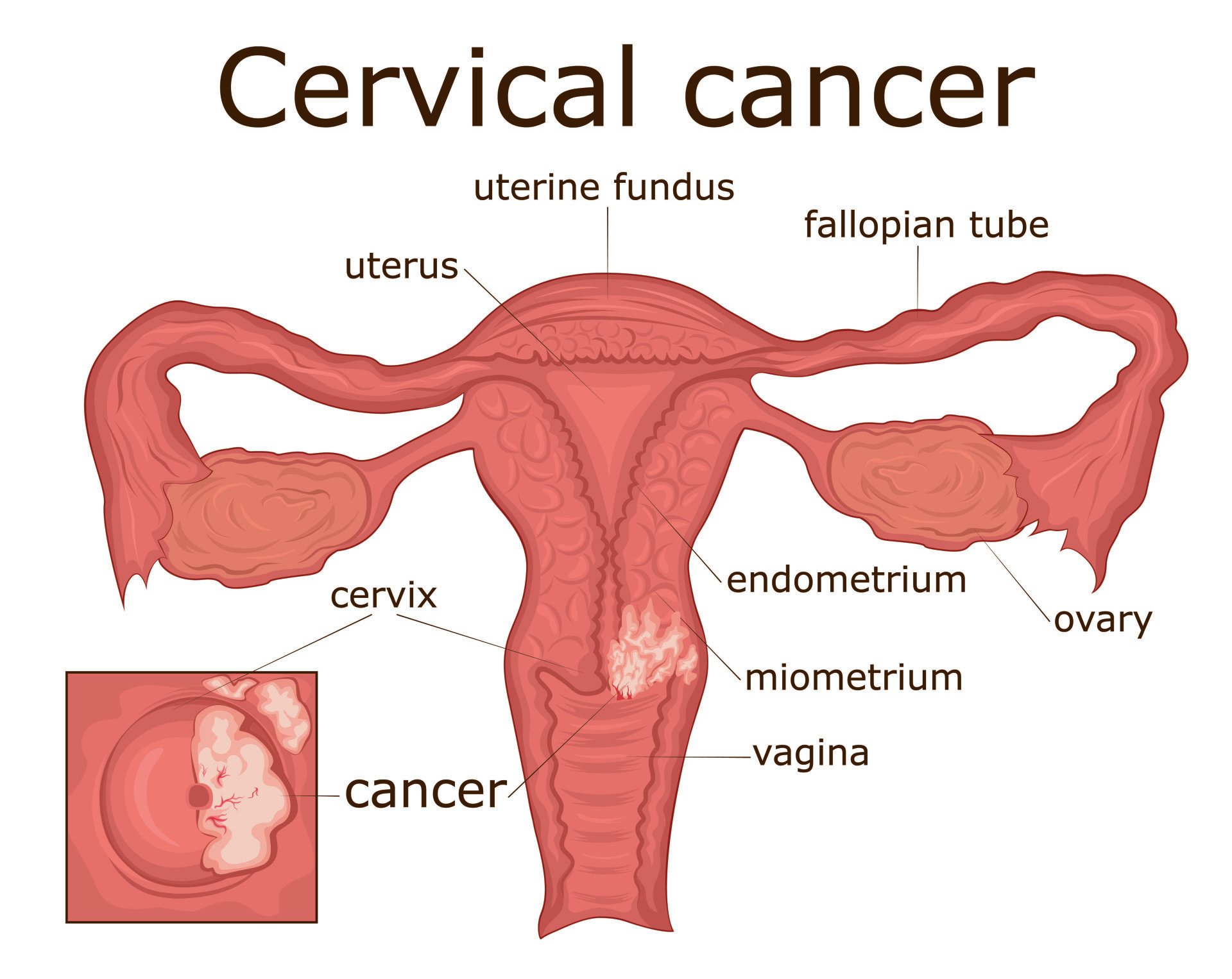
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is a type of malignancy that originates in the cervix, the lower part of the uterus connecting to the vagina. Typically caused by persistent infection with high-risk strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), cervical cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women worldwide. Early stages of the disease may not exhibit noticeable symptoms, emphasizing the importance of regular Pap smears for early detection.
Risk factors include a weakened immune system, smoking, long-term oral contraceptive use, and multiple sexual partners. Vaccination against HPV has emerged as a preventive measure. Symptoms may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, and discomfort during intercourse.
Treatment options vary depending on the stage but commonly involve surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Routine screenings and vaccination efforts are critical components of cervical cancer prevention and control programs, significantly contributing to improved outcomes and reduced mortality.
Esophagus Cancer
Esophageal cancer arises in the esophagus, the muscular tube connecting the throat to the stomach. Often diagnosed at advanced stages, symptoms include difficulty swallowing, weight loss, and persistent indigestion. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma, with risk factors including smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Diagnosis involves endoscopic procedures and imaging tests.
Treatment depends on the cancer stage but commonly involves surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Prognosis varies, with early detection significantly improving outcomes. Unfortunately, esophageal cancer is often diagnosed late, leading to a poorer prognosis. Prevention strategies include lifestyle modifications, addressing risk factors, and regular screenings for those with predisposing conditions. Ongoing research aims to enhance treatment options and raise awareness for early detection, crucial in improving the overall outlook for individuals facing esophageal cancer.

Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a prevalent form of cancer that develops in the prostate, a small gland situated beneath the bladder and in front of the rectum in men. The prostate plays a crucial role in producing seminal fluid. Prostate cancer often grows slowly and may not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, in advanced stages, it can lead to symptoms such as difficulty urinating, blood in the urine or semen, and discomfort in the pelvic area.
Risk factors for prostate cancer include age, with the likelihood increasing as men get older, family history, and race, with African-American men having a higher risk. While the exact cause is not fully understood, genetics and hormonal factors are believed to play a role. Early detection is typically through prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing and digital rectal exams.
Treatment options vary based on the stage of cancer and may include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these. Prostate cancer awareness, regular screenings, and ongoing research contribute to improved diagnosis and treatment outcomes for individuals affected by this condition.

Total Thyroidectomy
Total thyroidectomy is a surgical procedure involving the complete removal of the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck.
This procedure is commonly performed to treat thyroid cancer, large goiters, or certain thyroid disorders.
During the surgery, the entire thyroid gland is excised to ensure the removal of any existing or potential malignant tissue.
Total thyroidectomy may lead to the need for lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy to maintain essential metabolic functions.
Potential risks include damage to nearby structures such as the parathyroid glands, which regulate calcium levels, and the recurrent laryngeal nerve, affecting vocal cord function. Despite potential challenges, total thyroidectomy is often a crucial intervention to manage thyroid-related conditions and prevent the spread of cancer.
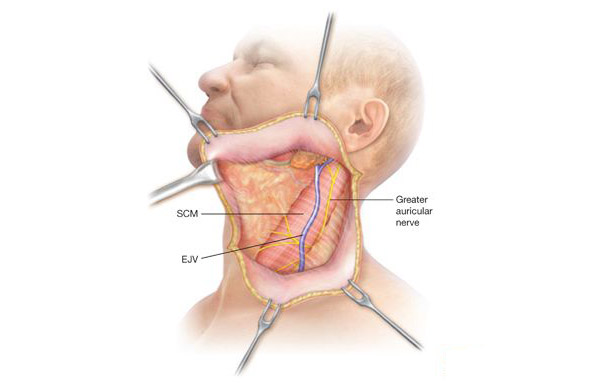
Neck dissection
Neck dissection is a surgical procedure involving the removal of lymph nodes and surrounding tissues in the neck.
This procedure is commonly performed to treat or prevent the spread of cancer originating in the head and neck region.
Lymph nodes are part of the body's immune system, and their removal is necessary when cancer has metastasized.
Neck dissection may be selective, removing specific lymph node groups, or radical, involving the removal of more extensive tissue.
Potential complications include damage to nerves, blood vessels, and the development of lymphedema.
Neck dissection plays a vital role in the comprehensive management of head and neck cancers, often complementing other treatments like surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.